Gluten might appear harmless, but for some individuals, it can silently provoke significant health problems. Often lacking clear warning signs, its impact may remain undetected, potentially causing long-term harm. Recognizing how your body responds to gluten is crucial for safeguarding your overall well-being.
CONTENT IS PROVIDED FOR INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED AS A SUBSTITUTE OF MEDICAL ADVICE.
SEEK GUIDANCE OF YOUR DOCTOR REGARDING YOUR HEALTH AND MEDICAL CONDITIONS.
1.
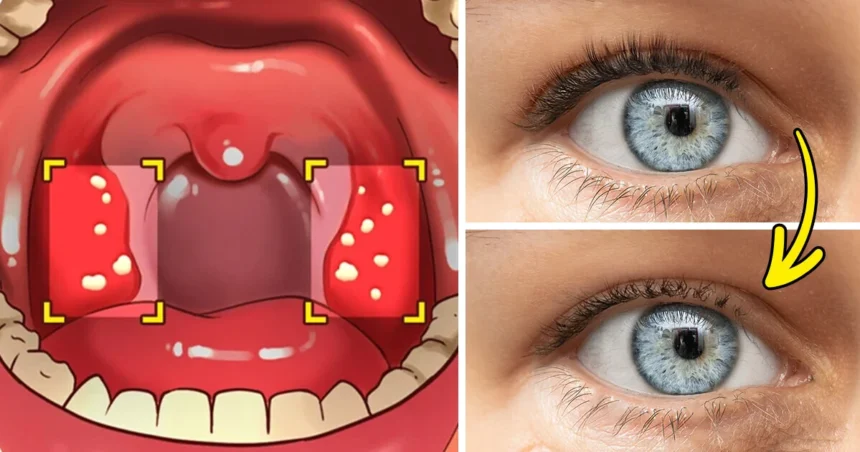
Alopecia
I think, I can never earn over which I paid by my precedent employer, but I was wrong, world is so large to try their fate. but now I am making $52/h even more, and easily earn minimum $1300/week, on the experience everyone must try to do work online, easy way to earn, here’s an example.
𝐰𝐰𝐰.Richnow1
Gluten intolerance, particularly in conditions like celiac disease, can lead to hair loss, including the loss of eyelashes. Additionally, gluten-induced damage to the small intestine can result in nutrient malabsorption, leading to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals like zinc, iron, and biotin, all crucial for healthy hair growth.
2.
Issues with the digestive system
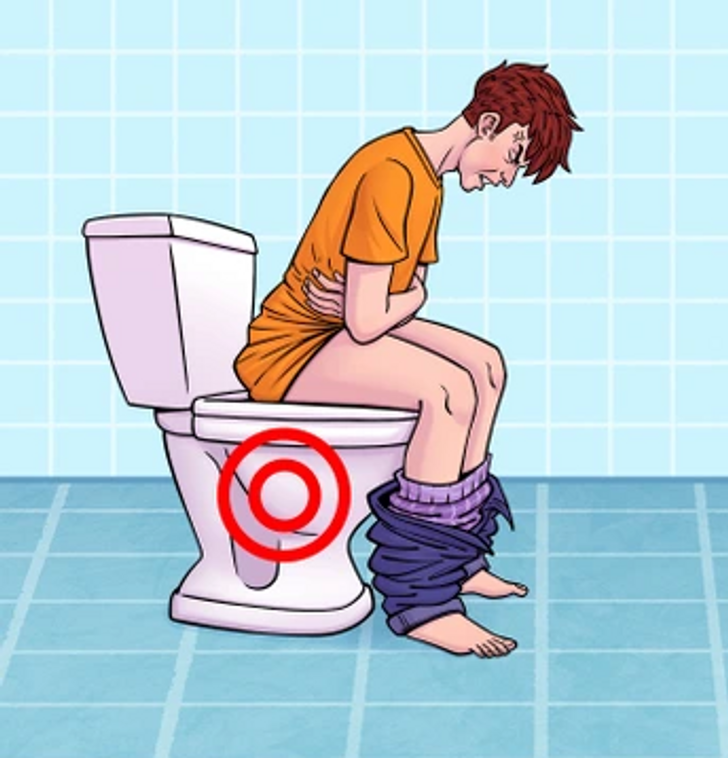

The symptoms of gluten sensitivity predominantly impact the digestive system, manifesting as nausea, bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and sometimes constipation.
These symptoms are frequently misinterpreted as signs of other conditions, leading to a common misdiagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Studies estimate that IBS affects 10-15% of the global population. However, for those with gluten sensitivity, such misdiagnoses can delay appropriate treatment, prolonging their discomfort and leaving their symptoms unaddressed.
3.
Weight changes
Gluten intolerance can trigger unexpected weight fluctuations, resulting in unexplained weight loss or gain. These changes are often driven by underlying inflammation at the cellular level and disruptions in normal metabolic processes. While abrupt weight changes can signal a range of health concerns, they may specifically suggest gluten intolerance when accompanied by additional symptoms related to nutrient malabsorption, such as fatigue, digestive issues, or deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
4. Hormonal imbalance issues

Gluten intolerance is strongly associated with hormonal imbalances, which can present as irregular menstrual cycles, unexpected weight fluctuations, premenstrual syndrome (PMS), and disruptions in sleep patterns. These hormonal irregularities often become more noticeable during pivotal life stages such as puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
Interestingly, these symptoms are most commonly observed in women, underscoring a potential gender-specific aspect of gluten intolerance’s impact on hormonal health.
5.
Issues with the central nervous system

Gluten consumption is linked to heightened inflammation and increased intestinal permeability, which can trigger a variety of neurological and psychological symptoms. These include difficulty concentrating, depression, anxiety, insomnia, fatigue, irritability, and the sensation of “brain fog,” where maintaining focus or mental clarity becomes challenging.
Additionally, research suggests that individuals with gluten intolerance are more prone to experiencing migraines than the general population. While headaches can arise from numerous factors, those with gluten sensitivity often report headaches after consuming gluten-containing foods, indicating a possible direct correlation.
6.
Skin problems

Gluten sensitivity is a chronic condition in which individuals with a genetic predisposition develop intolerance to gluten.
Its underlying mechanism is believed to be immune-mediated, and it can present with a range of dermatologic manifestations. Among the various forms of gluten intolerance, celiac disease (CD) is one of the most widespread, with potential effects extending beyond the gastrointestinal tract to include cutaneous, endocrine, neurological, and hematologic systems. Psoriasis, a separate chronic inflammatory skin disorder, has also been associated with marked symptomatic improvement following adherence to a gluten-free diet (GFD).
7. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder

The findings of this study suggest that a gluten-free diet can significantly improve ADHD symptoms, indicating that untreated celiac disease may increase the risk of mental and behavioral disorders such as ADHD.
8.
Poor condition of the teeth
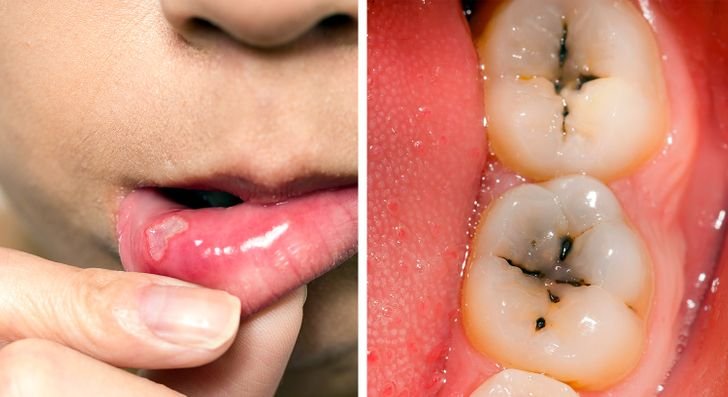
Gluten intolerance can interfere with the absorption of vital nutrients and minerals, including calcium, which is essential for maintaining oral health.
This malabsorption can contribute to issues such as enamel hypersensitivity, tooth decay, cavities, and recurrent mouth ulcers. If these dental problems persist despite good oral hygiene practices, gluten consumption could be an underlying factor, indicating a need to evaluate dietary habits and potential gluten sensitivity.
9.
Iron deficiency anemia

People with celiac disease often develop iron-deficiency anemia because they cannot adequately absorb iron from their diet. When individuals with celiac disease consume gluten, it triggers an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine, thereby impairing the absorption of nutrients—including iron.
10.
The story doesn’t end here — it continues on the next page.
Tap READ MORE to discover the rest 🔎👇